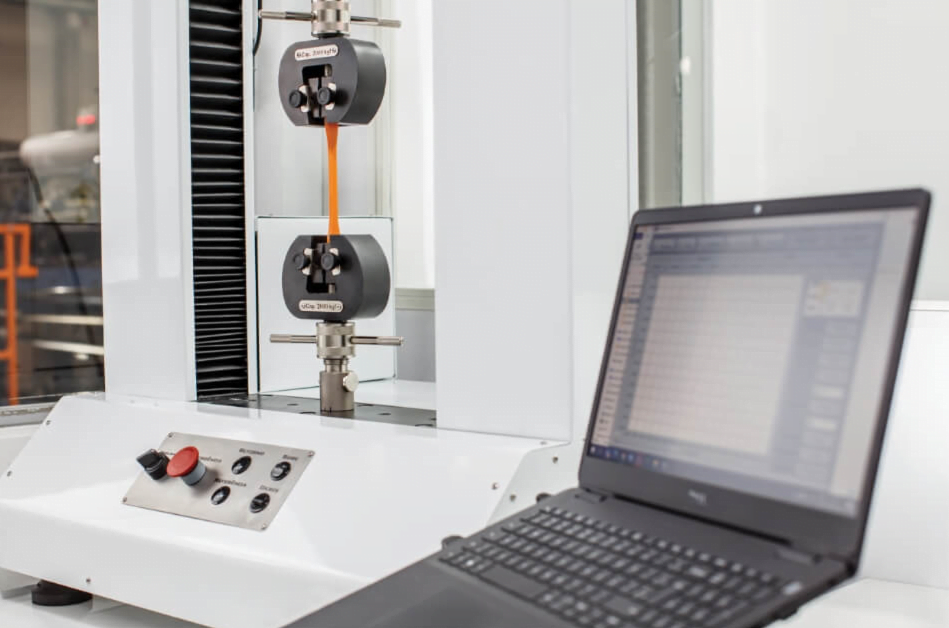
Learn more about the Lamiex laboratory and all the tests that are carried out to ensure the highest quality of the company’s products.
As you may already know, Lamiex specializes in producing laminate sheets of Polypropylene and Polyethylene. And to ensure the highest quality of our products, LAMIEX has invested in various laboratory equipment. This internal laboratory is intended to optimize internal studies, carry out comparative analyzes between materials, speed up the development of new products, assist in any investigations to find root causes of complaints, among other internal demands.
With the acquired equipment we were able to perform mechanical tests (tension, bending, compression, tear, abrasion), thermal tests (melt flow index, thermal expansion), physical tests (density, UV resistance, color and ash) and electrical tests (electrical resistance).
What equipment makes up the Lamiex laboratory?
As previously mentioned, Lamiex’s laboratory is composed of several pieces of equipment that allow different tests to be carried out on the company’s materials. The main ones include:
- Universal Testing Machine: used in tension, bending, compression, tear testing.
- Abrasion tester: used to measure abrasion.
- Plastometer: used to measure the melt flow index.
- Water bath: used to measure the coefficient of thermal expansion.
- Pycnometer: Used to measure density.
- Accelerated weathering chamber: used to measure UV resistance.
- Surface Resistivity Meter: Used to measure electrical resistance.
- Colorimeter: Used to measure color.
- Muffle: used to measure ash content.
Types of tests
Because it is well equipped, the Lamiex laboratory allows different types of tests to be performed on its premises. Next, we will talk in detail about each of them.
Mechanical Tests
Tension
Tension testing demonstrates the mechanical behavior of the material when it is subjected to axial forces (tensioning), that is, when the two ends of the specimen are pulled in opposite directions. This test determines the stress-strain curve, allowing the properties to be read:
- yield stress;
- yield elongation;
- ultimate tensile stress;
- ultimate tensile elongation;
- breaking stress;
- breaking elongation;
- area reduction;
- Young’s modulus.
Our tests are based on ASTM D638 methodology.
Bending
In this test, the specimen is supported at its two ends and an increasing mechanical load is applied to the center of the specimen, until it breaks or reaches a pre-established angle. This test determines the modulus of tension and the maximum tension supported by the specimen, important properties for the quality control of the material and for evaluating its performance when subjected to a flexural load. Our tests are based on ASTM D790 methodology.
Compression
The compression test determines the behavior of a specimen when compressed. This specimen is machined into a cylindrical shape and positioned between two sheets in the universal machine, when it is subjected to axial force in opposite directions, pressing the material. The properties that can be obtained from this test are:
- Elastic modulus;
- Yield stress
Our tests are based on ASTM D695 methodology.
Tear
The tear test indicates where the break is initiated and propagated when the specimen is subjected to tensile force in the universal machine. This test determines the tear strength of the material. Our test is performed based on ASTM D624.
Abrasion
This test presents the wear rate that the specimen undergoes when exposed to a certain friction. From this analysis it is possible to identify the materials with greater resistance to abrasion to indicate for applications that this type of wear can occur.
Thermal Tests
Melt Flow Index
This test is carried out in the plastometer, and indicates the amount, in grams, of the polymer that is extruded, under standard conditions, in a period of 10 minutes. This result represents the ease of flow of the molten resin.
thermal expansion
This test demonstrates the behavior of the material when exposed to different temperatures. The test consists of exposing a specimen to certain temperatures and verifying the dimensional variation that the body undergoes. This information is important for products that will be exposed to different temperatures, which could compromise the process if this property is not studied.
Physical Tests
Density
Density testing is widely used for quality control, to verify batch uniformity, to assess physical changes in a sample, to define the application of certain materials, etc.
UV resistance
This test is performed to determine the period that a material can be exposed to UV light without degrading or having its mechanical properties impacted. It is carried out in parallel with other analyses, for example tension, bending, compression, it all depends on the purpose of the material to be tested.
Color test
Color perception varies between each observer, the light interacts with an object that is thus perceived by the human eye. Besides the light factor, color is a psycho-visual process, that is, it is the way the brain interprets the light capture by the eyes. Because it is a subjective phenomenon, this test aims to accurately describe the color of a material, helping quality control in many areas where color is paramount in the process, such as plastics manufacturing, for example.
Ash content test
This test aims to determine the amount of inorganic filler present in the formulation. The fillers have several functions when inserted in the polymeric matrix, being able to serve as filler, to reduce cost, for mechanical reinforcement, among others. This test is based on ASTM D5630 methodology.
Electrical tests
Electricity resistance
This test measures how resistant a plastic material is to the flow of electric current. This analysis is important for choosing the ideal material for applications that require certain behavior, such as insulation or conduction as required characteristics. Electrical wire covers, for example, must be electrically insulating to allow them to be handled.